Bone cancer originates from normal cells within a bone. While it can start in any bone, it most commonly affects the long bones of the legs, particularly the thigh bone. It’s important to understand that “bone cancer” does not include cancers that start in other parts of the body and then spread to the bones. These are named after their original site. For instance, cancer that begins in the lungs and spreads to the bones is referred to as lung cancer with bone metastasis.
What is Bone Cancer?
Bone cancer is relatively rare, and different types affect people differently based on age. Some types are more prevalent in children, while others occur primarily in adults. The rarity and complexity of bone cancer make it essential to be informed about its types, symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Types of Bone Cancer
Bone cancers are classified primarily based on the type of cell where the cancer originates. The most common types include:
- Osteosarcoma: This is the most common type of bone cancer, originating in the cells that form bones. Osteosarcoma typically affects teenagers and young adults, though it can also occur in younger children and older adults. It frequently appears in the long bones of the legs and occasionally in the arms. Rarely, it can develop in soft tissues outside the bones.
- Chondrosarcoma: Chondrosarcoma usually begins in the bones but can sometimes start in the soft tissues. This type of cancer is most common in middle-aged and older adults and typically affects the pelvis, hip, and shoulder.
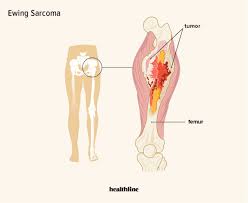
- Ewing Sarcoma: Ewing sarcoma can start in both the bones and the surrounding soft tissue. It often affects children and teenagers but can occur at any age. This cancer most frequently begins in the leg bones and pelvis, though it can appear in any bone.
Symptoms of Bone Cancer
- Bone ache: This is frequently the first symptom, and it can be persistent or come and pass. The pain may worsen at night time or in the course of bodily activity.
- Swelling and tenderness: Swelling close to the affected location can arise, frequently along with tenderness to touch.
- Weakened bones: Bones might also grow to be fragile, mainly to fractures from minor accidents.
- Fatigue: A well known feeling of tiredness that doesn’t improve with relaxation.
- Unexplained weight reduction: Losing weight without trying also can be a sign of bone cancer.
When to See a Doctor
If you revel in any of the above symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional right away. Early analysis can considerably affect treatment consequences. Make an appointment with a medical doctor when you have continual bone ache, swelling, or every other concerning signs and symptoms.
Risk elements for bone cancer include:
- Inherited genetic syndromes: Certain rare genetic conditions, such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome and hereditary retinoblastoma, can increase the risk of developing bone cancer.
- Other bone conditions: Diseases like Paget’s disease of bone and fibrous dysplasia may also elevate the risk.
- Previous cancer treatments: Radiation therapy and specific chemotherapy drugs used to treat other cancers can increase the risk of bone cancer later in life.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing bone cancer normally entails a combination of imaging tests (like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs) and biopsies, in which a pattern of the tumor is examined underneath a microscope. Blood assessments will also be performed to test for markers associated with bone most cancers.
Treatment options depend on the type of bone cancer, its location, and its stage. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: The goal is to remove the entire tumor. This may sometimes involve reconstructive surgery to repair the bone.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells. This treatment is often used before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: This involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy is frequently used for cancers that have spread or are at high risk of spreading.
Coping with Bone Cancer
Facing a bone, most cancers analysis can be overwhelming. It’s important to have an aid system in place that can encompass family, buddies, aid companies, and healthcare experts. Managing aspect effects, keeping a wholesome lifestyle, and staying knowledgeable approximately your condition also can assist in managing the sickness.
Conclusion
Understanding bone most cancers, its types, signs and symptoms, and remedy options is vital for early detection and effective management. While bone cancer is uncommon, consciousness and prompt medical interest could make a sizable distinction in effects. If you or someone you realize is experiencing signs, do not hesitate to try to find a medical recommendation.