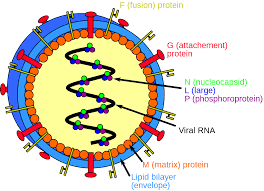
Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus, meaning it spreads between animals and humans. This virus in general circulates amongst fruit bats, also called flying foxes, but it may also infect other animals like pigs, goats, horses, dogs, and cats. Human infections frequently occur because of direct or oblique touch with inflamed animals or their physical fluids (blood, urine, feces, or saliva). Additionally, consuming meals contaminated by inflamed animals or near touch with an infected individual can result in Nipah virus transmission.
Modes of Nipah Transmission
- Animal to Human: Nipah virus spreads from animals to human beings via contact with the physical fluids of inflamed animals. This regularly involves fruit bats or pigs. For instance, people may also turn out to be infected by consuming culmination infected with bat saliva or through managing ill pigs.
- Human to Human: The virus also can unfold from character to individual via direct contact with bodily fluids like saliva, urine, blood, or respiratory droplets. Caregivers and healthcare people are at higher chance, mainly if they do not use a defensive system.
Nipah Symptoms and Severity
The signs of Nipah virus infection can variety from slight to severe. Initially, inflamed people can also experience:
- Fever
- Headache
- Breathing problems
- Cough and sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Muscle pain and excessive weak point
These signs and symptoms typically appear four to 14 days after exposure to the virus. In intense instances, the infection can development to encephalitis, an inflammation of the mind, which can result in:
- Confusion and disorientation
- Slurred speech
- Seizures
- Coma
- Respiratory distress
Nipah Preventive Measures
- Avoid Contact with Sick Animals: In areas with acknowledged Nipah virus outbreaks, avoid touch with bats and pigs. Ensure that farms are smooth and disinfected, and unwell animals are quarantined.
- Food Safety: Avoid consuming uncooked date palm sap and culmination that can be infected with bat fluids. Always wash and peel fruits earlier than consumption, and discard any fruit with bat bites or those observed on the floor.
- Hand Hygiene: Wash fingers regularly with cleaning soap and water, particularly after handling animals or getting into touch with doubtlessly infected surfaces.
- Protective Equipment: Use a non-public protective system (PPE) consisting of gloves, mask, robes, and eye safety whilst worrying for inflamed individuals.
Nipha Outbreak History and Geographic Distribution
Nipah virus first recognized in 1999 through a pandemic in Malaysia and Singapore, which led to a hundred deaths and brought about the culling of over one million pigs to govern the spread. Since then, there have been almost 20 outbreaks, more often than not in Bangladesh and India. Other areas like Cambodia, Indonesia, Madagascar, the Philippines, and Thailand also are at risk because of the presence of fruit bats that carry the virus.
Nipah Recent Outbreak in Kerala, India
A recent outbreak in Kerala, India, highlighted the persistent chance of Nipah virus. In July 2024, a fifteen-12 months-antique boy from Malappuram district died from the virus, leading to an in-depth public fitness response. The Kerala Health Department identified 350 humans at the touch listing of the deceased, with one zero one of them classified as excessive-danger. Efforts protected sending samples for trying out, setting apart symptomatic individuals, and conducting house-to-residence surveys in affected areas.
Managing Nipah Virus Infections
Since there is no specific antiviral treatment for Nipah virus, management focuses on supportive care to relieve symptoms. This includes:
- Hydration: Ensuring the affected person stays hydrated by way of ingesting plenty of water.
- Rest: Encouraging the patient to rest to assist their body fight the infection.
- Medications: Using ache relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, anti-nausea tablets, inhalers or nebulizers for breathing troubles, and anti seizure medicines if necessary.
Researchers are exploring using monoclonal antibodies as an ability treatment for Nipah virus, however currently, handling signs and symptoms remains the primary technique.
Nipah Importance of Vigilance and Preparedness
Preventing Nipah virus outbreaks requires vigilance and preparedness. Public fitness authorities should enforce strict infection control measures, including the usage of PPE, disinfecting surfaces, and setting apart inflamed people. Communities in regions at risk should be knowledgeable about the virus and the significance of warding off contact with ill animals and ingesting contaminated meals.
Conclusion
Nipah virus poses a vast risk due to its excessive fatality charge and the capacity for fast unfolding. Understanding the modes of transmission, signs and symptoms, preventive measures, and the significance of vigilant public fitness efforts is vital in mitigating the impact of this deadly virus. As research continues, there’s a wish for more powerful remedies and possibly a vaccine within the future. In the period in-between, focus and precaution are our excellent defenses towards Nipah virus.
Any Symptoms Consult a Doctor – Best Doctor Consultation Services at Home in Trivandrum| Kochi